As an expert in infectious diseases, editor of the Journal of Infectious Diseases and author of the textbook Infectious Diseases: A clinical short course, McGraw-Hill April 2020, I have been concerned about the misinformation being shared about the COVID-19 epidemic. How did this disease develop? Where did it come from? How does it cause diseases? The answers to these questions will be answered in the first video of module 1. The world has been startled and frightened by the rapid spread of this virus throughout the world. In Video 2 the epidemiology as presently understood is reviewed. This video will be periodically updated recognizing the rapid progression of the pandemic. Many want to know how does this disease present, what are the symptoms associated with COVID-19? How dangerous is COVID-19? Who is at risk of dying? All these questions are answered in Video 3. And finally how is this disease best treated and how can we slow the spread of the infection? These questions are answered in video 4. In addition to the videos multiple choice questions are included to test your understanding and there is an epidemiology peer reviewed exercise designed to teach you how this infection is spread and to show the power of the tracing of cases and isolating those who are infected. The second peer review exercise will encourage you to create a campaign to shift your countries culture to embrace behaviors that can lead to suppression of the epidemic, behaviors that will save lives. After completing this course you will be armed with the knowledge and skills to make a difference and help to bend the curve.



COVID-19 - A clinical update

Instructor: Frederick S. Southwick, MD
Access provided by Coursera Learning Team
23,886 already enrolled
(342 reviews)
Recommended experience
What you'll learn
Understand how this coronavirus invades respiratory epithelial cells, grows in the nasal passages and spreads to alveoli to cause hypoxia.
Describe what makes this coronavirus so infectious, how it has spread quickly throughout the world and how best to stop its spread.
Recognize the clinical symptoms of COVID-19 disease and be able to diagnose this disease
List the recommended treatments for COVD-19, as well as the treatments under investigation
Skills you'll gain
Details to know

Add to your LinkedIn profile
2 assignments
See how employees at top companies are mastering in-demand skills


Earn a career certificate
Add this credential to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV
Share it on social media and in your performance review

There are 2 modules in this course
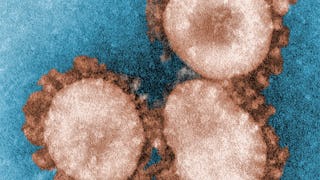
Coronaviruses infect many species of animal including the bat. These RNA viruses frequently mutate particularly in bats, and chance mutations rendered the SARS-CoV-2 capable of readily infecting humans. The bat virus infected an intermediate host, possibly the Pangolin that was sold in the live fish and animal market in China. A key virulence (characteristic that allows a pathogen to cause disease) factor is the S protein which was the likely primary target of the mutations. This protein forms knobs on the outer surface of the virus that bind strongly to the ACE2 receptor on human respiratory epithelial cells. Binding is followed by internalization and within the cell the virus replicates its RNA using a replicase and assembles into a nuclear capsid in the host cell cytoplasm RNA is also translated into proteins that coat the outer surface of the virus. Once fully assembled the virus is exocytosed (released) from vesicles. The new viral particles can infect other cells and spread to other humans. Because of the inaccuracy of the viral replicase as the virus actively grows it produces point mutations. Some of these mutant virus more effectively infect cells. The alpha variant became prominent in the Winter and Spring of 2021 subsequently a more highly infectious variant the Delta variant that originated in India dominated and now a third variant, omicron that originated in South Africa is now spreading throughout the world and quickly dominating in Europe and the U.S. The virus first replicates in the throat and nasal passages and then spreads to the trachea, bronchi and alveoli where it induces inflammation and damage to the alveolar walls causing fluid to leak into the air exchanging sacks and interfering with oxygen exchange. If inflammation continues the alveolar walls become fibrosed (scarred) and further compromising oxygen exchange resulting in decreases in oxygen saturation (hypoxia). SARS-CoV-2 is able to spread efficiently from person to person primarily by droplets and aerosol (tiny particles that stay in the air for hours). Infection quickly spread throughout the world and caused a pandemic within 3 months. Humans were infected at the Huanan live fish and animal market. The infection initially was confined to workers in the market (point source) but then quickly spread person to person within the first 10 days. Because of the lack of travel restrictions early in the outbreak Chinese traveling from the area quickly spread the virus to many other countries. In the early phases lack of therapy or vaccine allowed the virus to move from person to person unchecked with a steep exponential curve with a doubling of cases every 2-3 days. This virus is one of the most infectious ever reported each infected person on average infecting 2.0 to 2.7 people, the alpha variant can infect 3.0-5.0, the Delta variant one person on average infects 5-8 individuals and the omicron 10-16. The last two variants can cause breakthrough infections in vaccinated individuals. Another characteristic that has allowed rapid spread is the existence of 40-60% asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic carriers. 10% are superspreaders infecting on average 10-80 others.
What's included
5 videos2 readings1 assignment1 peer review
COVID-19 presents similarly to influenza. The most common symptoms are fever (>100.4 °F or 38°C), dry cough, and shortness of breath. Other common symptoms include marked fatigue, myalgias (muscle aches), headache, and sorethroat. Chest tightness can develop early in severe cases. Diarrhea and vomiting less commonly can be presenting complaints. Physical exam is usually unremarkable with the exception of fever, tachycardias (elevated pulse), an elevated respiratory rate and low oxygen saturation on room air. Lymphadenopathy is usually not present and pulmonary exam is unremarkable. Laboratory studies are nonspecific with a low lymphocyte count, low platelets, elevated CRP, and normal procalcitonin level. CXR is insensitive (60% sensitivity) chest CT being more sensitive and highly specific and is the study of choice in patients being considered for admission to the hospital. Treatment consists of supportive care by administering nasal O2 to maintain saturation above 92%. If nasal O2 fails to achieve appropriate oxygenation intubation and mechanical ventilation with PEEP (positive end expiratory pressure) is recommended and standard ARDS protocols should guide care. Septic shock with end organ damage can develop and standard sepsis protocols are recommended with the exception of fluid administration which should be cautious.
What's included
6 videos1 reading1 assignment
Instructor

Offered by
Why people choose Coursera for their career




Learner reviews
342 reviews
- 5 stars
78.36%
- 4 stars
16.66%
- 3 stars
2.33%
- 2 stars
0.58%
- 1 star
2.04%
Showing 3 of 342
Reviewed on Jun 21, 2020
A very informative course regarding the ongoing pandemic! Although it just needed some update due to recent data and studies. The instructor is great!
Reviewed on Jun 13, 2020
This course is really instructive and interesting.Very well designed and organized.It could be improved by giving more in-depth knowledge. Thankyou!
Reviewed on Apr 20, 2020
very informative regading the methods of diagnosis , what is upto date regarding treatments and why staying at home matters
Recommended if you're interested in Health

Imperial College London
American Museum of Natural History

Xi'an Jiaotong University

Open new doors with Coursera Plus
Unlimited access to 10,000+ world-class courses, hands-on projects, and job-ready certificate programs - all included in your subscription
Advance your career with an online degree
Earn a degree from world-class universities - 100% online
Join over 3,400 global companies that choose Coursera for Business
Upskill your employees to excel in the digital economy



